Table of Contents For Bitumen 60 70
Premi Quality Bitumen 60 70 - Guaranteed Satisfaction
Bitumen, a term that originated in the Sanskrit word “jatu-krit,” which means sticky, remains an essential ingredient for construction even in ancient periods. Out of all the grades that are in use today, bitumen 60/70 has gained importance in contemporary road construction and paving. In this article, the reader will find information about the properties of BC 60/70, its production and application, and possible further evolution. The following article will be of immense help to civil engineers, contractors, or any user who needs more information about this flexible construction material.
What is Bitumen 60/70?
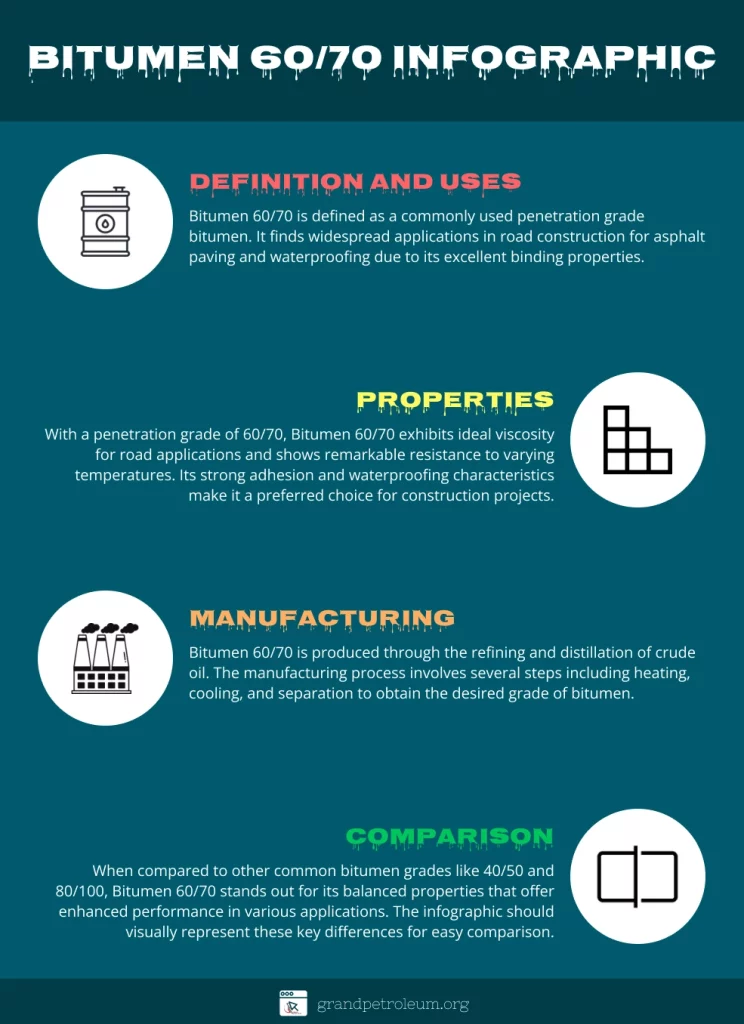
Bitumen is a viscous material, which is a natural derivative of crude oil and remains after the process of distillation. Crude oil is largely made up of a diverse group of chemical components referred to as asphaltenes and maltenes. The “60/70” indicates the grade in terms of penetration, which measures the uniformity and hardness of the substance.
The penetration value is calculated as the number of units in tenths of a millimeter up to which a standard needle penetrates through a sample of bitumen during the specific temperatures, load and time depending on the standard either ASTM D5 or EN 1426 has been followed. It has a penetration value of 60/70 at an operating temperature of 25°C, thus making it semi-solid but flexible for paving.
Some of the properties of 60/70 penetration grade Bitumen include the following;
Bitumen 60/70 exhibits several essential properties that make it suitable for various construction applications:
Softening Point: This is the temperature at which bitumen melts and thus can be used, although the commonly used 60/70 grade is expected to melt between 46°C and 54°C for 60 minutes.
Ductility: The capacity to extend to be as slim as a slim plastic thread prior to getting brittle and separating, expressed in centimeters. Ductility, on the other hand, enables the material to bend without breaking and increases the resistance to crack formation.
Viscosity: One of the factors that makes the flow more difficult to maintain is the fact that the level of resistance decreases with the increase in temperature. Workability during construction is also affected by the viscosity or the material’s ability to be pumped.
Flash Point: The lowest temperature at which the vapors of bitumen can be made to burn, which is an important factor in determining how it may be stored and used.
Solubility: The nature of the ability of bitumen to dissolve in specific solvents and its compatibility with other materials.
These properties should always be met so as to guarantee uniformity along with the quality of the bitumen 60/70 in every use. Bitumen 60/70 is a versatile product mostly used in construction and infrastructure projects since it has a high penetration capacity and is resistant to different weather conditions.
Road construction and flexible pavements are the most common areas where bitumen grade 60/70 is used and mainly function in binding aggregates used in asphalt concrete mixes. Its penetration value allows it to be used in moderately sealed environments, and its temperature sensitivity makes it ideal for areas with moderate differences in climate.
Other applications of bitumen 60 70 include:
- Waterproofing and damp-proofing membranes
- Sealants and joint fillers
- Roofing and insulation materials
- Pavement preservation and maintenance
The application of bitumen 60/70 can be attributed to the fact that it may be modified using polymers or other added materials, and this improves its performance depending on the required use.
ELIGIBLE CRUDE AND PROCESSING OF 60/70 PENETRATION GRADE BITUMEN
Bitumen 60/70 is obtained from crude oils through various refining techniques, which is why this product. The primary steps involved are:
Atmospheric Distillation: The crude oil is then heated and broken into different fractions, referred to as other leaves, and the heaviest fraction is known as atmospheric residue or long residue.
Vacuum Distillation: When heated under vacuum distillation, the heavier components of the atmospheric residue are evaporated, leaving behind the vacuum residue or short residue.
Air-Blowing or Oxidation: After de-including, the vacuum residue is exposed to controlled air blowing/ oxidation in order to fine-tune the penetration value as well as other properties to achieve the required 60/70 grade.
High temperatures, pressures, and the right time duration in the said stages help achieve the desired properties of the final bitumen product in most plants.
Transportation, Storage and some measures that should be taken while working with Fentanyl and other related compounds
Measures concerning the storage of bitumen 60 70 also need to be considered to prevent compromising its quality and endangering the lives of workers. Here are some key considerations:
Storage Tanks: Little mention was made about the pump diluent or thinner, which is bitumen, and it should be stored in insulated tanks with provisions for heating coils to contain the required temperature of between 150-180° C.
Heating and Handling: Exposing the material to temperatures that are higher than its range results in oxidation and an increase in temperature to the point that the binder becomes harder, and some of its desirable characteristics begin to deteriorate.
It is important to stay safe and follow all the recommended measures and procedures when dealing with bitumen 60 70 to avoid being exposed to possible dangers and also to keep the quality of the product high.
Bitumen can be obtained with varying penetration grades, which determine its employment and compatibility with the climate. Here’s how bitumen 60/70 compares with some common grades:
Grade Penetration Value (0. 1 mm) Typical Applications40/5040 – 50Warmer climates, used in heavy trafficked roads, airports and affluence towns60/7060 – 70Used in moderate climates for flexible pavements and busty traffic roads80/10080 – 100Cold climate for low traffic roads
Alkenides like 40/50 are slightly more appropriate for regions with high temperatures and high traffic volumes, while bitumens like 80/100 should be used in cold climates with low traffic flow volumes. Bitumen 60/70 is the most suited type because it is generally suitable for all types of pavements under moderate climatic conditions.
Recent developments, advancements and future possibilities
Research reveals that the development of the bitumen industry is dynamic and responsive to performance issues, sustainability, and construction requirements. Some notable innovations and trends include:
Polymer-Modified Bitumen (PMB): Other polymers, which, when blended with bitumen, improve the properties of bituminous mixtures include styrene-butadiene-styrene (SBS) or ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA), which boosts its elasticity, resistance to deformation, and endurance.
Warm Mix Asphalt (WMA): These technologies facilitate the production and laying of asphalt at lower temperatures; hence, less energy is used, and the emission rate is low.
Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement (RAP): We aim to improve the incorporation of recycled materials into new mixtures and paving materials and examine and analyze how best this can be done to ensure sustainability and better conservation of natural resources.
Bio-Based Bitumen Modifiers: We interact with experts in the petrochemical industry to understand the possibility of implementing bio-derived additives and modifiers through the usage of renewable feedstock to reduce the carbon footprint in bitumen production.
Advanced Testing Methods: Bitumen behavior will be determined by comparing the use of new test methods, such as multiple stress creep recovery (MCSCR) and linear amplitude sweep (LAS).
With increasing developments in the construction industry, bitumen 60/70 and all its relevant types will continue to be useful and resourceful in present and future construction projects and developments with a focus on sustainability and environmental conservation.

Durability and Performance: Bitumen 60 70 as a Paving Material
Road construction is one of the most important processes, and one of the main objectives is the durability and performance of the pavement material during its use. By having the appropriate grading, Bitumen 60/70 gives a strong performance that can handle traffic load and withstand the wear and tear that comes as a result of climate changes for a longer duration.
Rutting and deformation are usually associated with the resistance of pavement layers to traffic loads and forces which are exerted on the pavement surface during its service life.
Rutting, or the formation of permanent depression in the wheel paths, is by far one of the most prevalent problems that flexible pavement surfaces experience. The penetration value of bitumen 60/70 is one of the factors that determine how well it can minimize this problem. Its semi-solid nature at the temperature of the atmosphere enables it to have adequate support of the mixture structure under traffic load at a given site against permanent deformation.
Moreover, it is equally important to add polymer modifiers that include SBS or EVA, which have the ability to improve the rutting resistance of the bitumen 60/70. These polymers enhance the elasticity of the binder so that the binder can bounce back from deformation states that could be temporary in nature.
Fatigue Cracking Resistance
Fatigue cracking, which is the cracks that connect the pavement surface, is another major problem with flexible pavements. In extreme cases, they expand over time, allowing for the occurrence of structural failure and reduced pavement strength. Bitumen 60/70 also has a very low rate of fatigue cracking due to the high ductility and flexibility of this asphalt.
The ductility of bitumen 60/70 allows it to accommodate the tensile strains induced by traffic loading and thermal cycling without cracking. This property becomes increasingly important in areas with significant temperature variations, where the pavement is subjected to thermal stresses.
Aging and Oxidation Resistance
Bitumen also experiences a process where its properties change due to various factors such as ageing and oxidation, where it hardens and becomes brittle. It can also contribute to the increase in the susceptibility of the pavement to cracking and other forms of distress. Bitumen 60/70: Its formulation and the process of production take into consideration the conditions that could cause ageing and oxidation.
The air-blown or oxidation process in the refining process relates a definite measure of oxidation to make the end product a heat-resistant and long-lasting bitumen. Also, antioxidants and other additives can be added to increase resistance to oxidative ageing, consequently increasing the lifespan of the pavement.
Bitumen 60/70 Infographic
Moisture Resistance and Stripping
Stripping or moisture damage is another phenomenon that is widely reported on asphalt pavements, whereby water gets into the contact area of aggregate and bitumen, leading to de-bonding. This can lead to problems such as raveling, the formation of potholes, and even the general deterioration of the pavement structure. Bitumen 60/70 has a chemical composition that allows it to resist moisture damage, and its surface properties also have an influence.
This is because the bitumen forms a good interface with the anti-stripping agents, such as hydrated lime or liquid anti-stripping additives, hence making it adhere well to the aggregate particles. Further, the right types of aggregates and the right size of aggregates can also contribute towards increasing the moisture susceptibility of the asphalt mixture.
Construction Considerations
However, bitumen 60/70’s performance characteristics go hand in hand with benefits related to the construction process. Its suitable viscosity at normal paving temperatures of between 150 – 180 o C makes it easily mixable, placeable and compatible.
The temperature susceptibility of bitumen 60 70 provides some flexibility in working beneath the optimum temperature, where contractors can compact the mixture to the required density and achieve a smooth surface before the binder becomes too brittle. This characteristic is partly responsible for the quality, flatness and uniformity of the final pavement surface.
Conclusion
The overall findings of this research reveal that bitumen 60/70 is a versatile and greatly used material in paving that possesses the right and desired characteristics for use in different climates and construction types. This article provides a general overview of this grade of bitumen, from its production and refining processes to how it should be handled and safely used in construction projects. It is very important for civil engineers and contractors. In the modern construction industry, modification, testing and improvement of bitumen 60/70 will remain relevant due to the development of new technologies that will define the use of the material in the construction of modern infrastructures.
FAQ
Bitumen 60/70 is a type of asphalt known for its specific viscosity and penetration grade, commonly used in road construction and waterproofing projects. It has a penetration grade between 60 to 70 mm, indicating its softness.
Bitumen 60/70 is widely used in the construction and maintenance of roads and for waterproofing buildings. Its physical and chemical properties make it suitable for use in warm and moderate climates.
The quality of Bitumen 60/70 is assessed through standard tests such as penetration grade, softening point, and solubility in specific solvents. These tests ensure that the product meets the required standards for various applications.
Bitumen 60/70 is produced through the refining of crude oil. The production process involves separating light and heavy components of crude oil and processing them to achieve the desired physical and chemical properties.
The primary difference between Bitumen 60/70 and other types of bitumen is in its penetration grade and softening point. These characteristics make Bitumen 60/70 suitable for use in areas with high temperatures, whereas other types of bitumen may be better suited for different climatic conditions.
Like other petroleum derivatives, Bitumen 60/70 can have environmental impacts. Proper precautions should be taken during its use and storage to prevent spills and environmental contamination.
Bitumen 60/70 should be stored in a dry, cool place away from direct sunlight. Storage in airtight, weather-resistant containers can help maintain its quality.
To order Bitumen 60/70, you can visit our website and fill out the online order form, specifying the quantity and specifications you need. Alternatively, you can contact our sales team directly by phone or email to discuss your requirements and receive a personalized quote. We offer flexible shipping options to accommodate your delivery needs.
